Ford Mustang (1999-2004) Service Manual: Shift Patterns
Upshifts
Transmission upshifting is controlled by the powertrain control module (PCM). The PCM receives inputs from various engine or vehicle sensors and driver demands to control shift scheduling, shift feel and torque converter clutch (TCC) operation.
Downshifts
Under certain conditions the transmission will downshift automatically to a lower gear range (without moving the gearshift lever). There are three categories of automatic downshifts; Coastdown, Torque Demand and Forced or Kickdown shifts.
Coastdown
The coastdown downshift occurs when the vehicle is coasting down to a stop.
Torque Demand
The torque demand downshift occurs (automatically) during part throttle acceleration when the demand for torque is greater than the engine can provide at that gear ratio. If applied, the transmission will disengage the TCC to provide added acceleration.
Kickdown
For maximum acceleration, the driver can force a downshift by pressing the accelerator pedal to the floor. A forced downshift into a lower gear is possible below calibrated speeds. Specifications for downshift speeds are subject to variations due to tire size, engine and transmission calibration requirements.
Disassembled Views
4R70W Automatic Transmission - Disassembled View
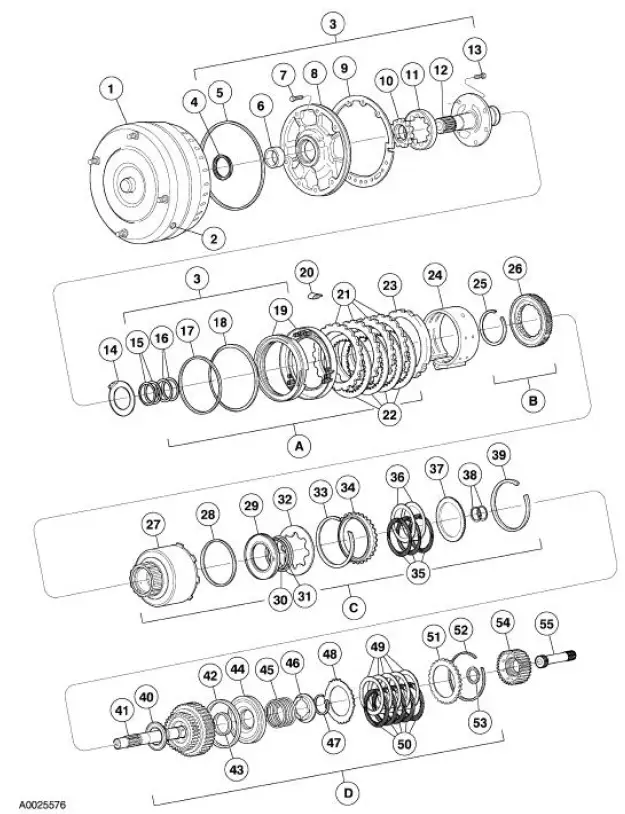
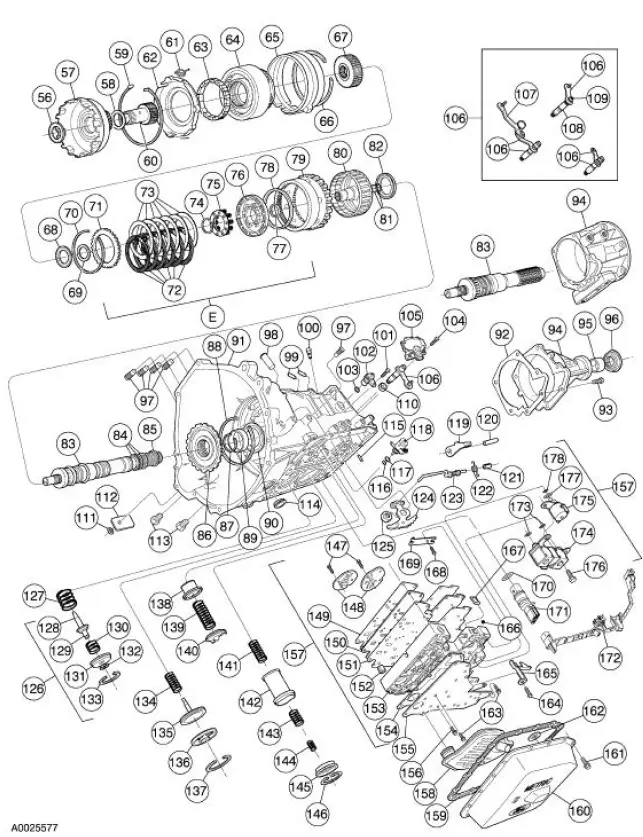
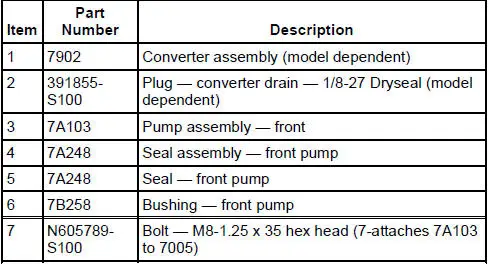
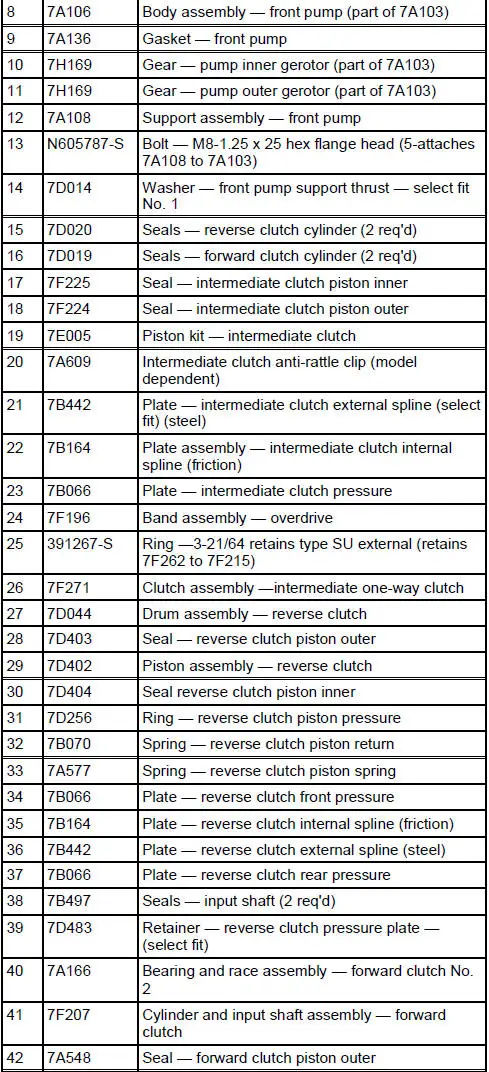
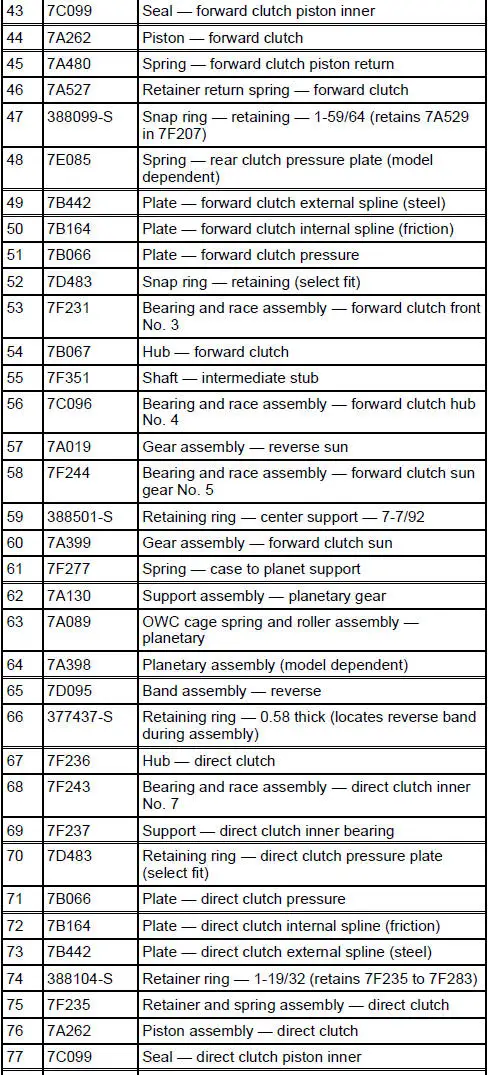
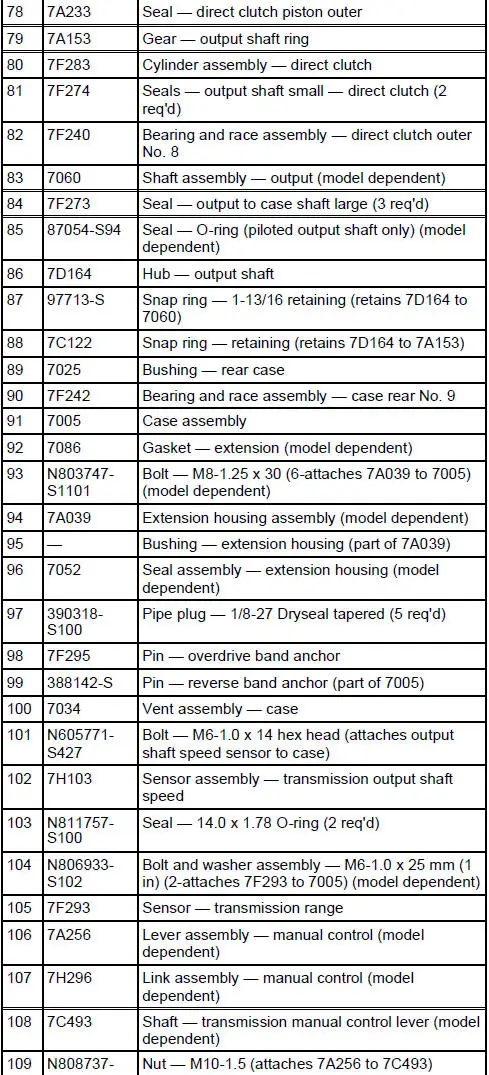
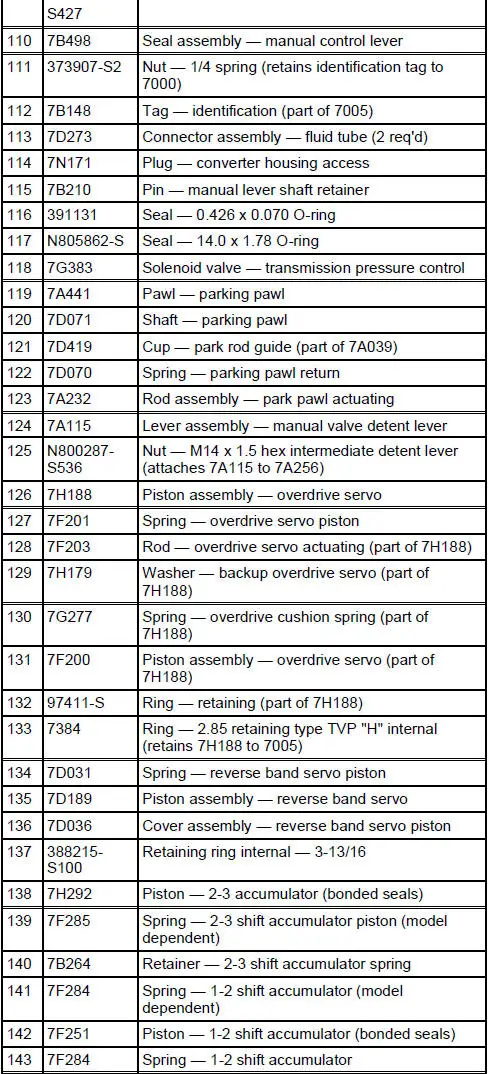
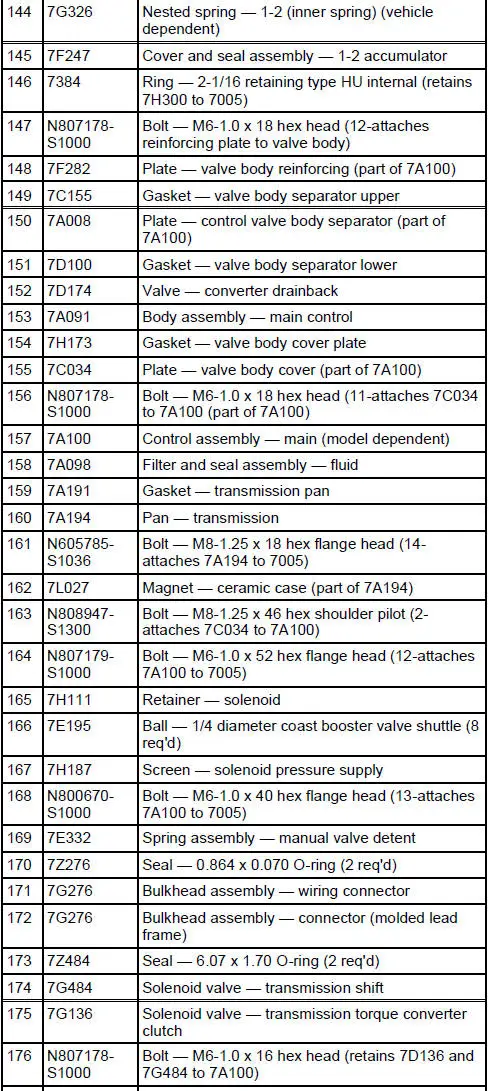
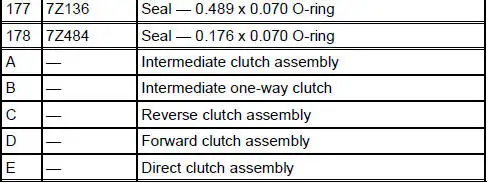
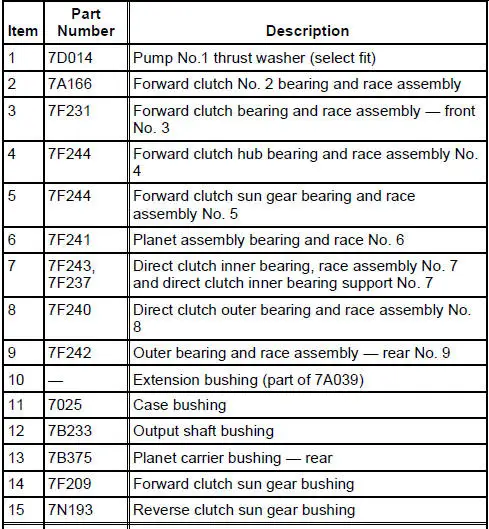
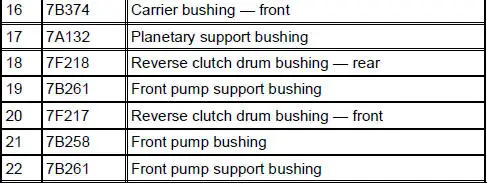
Bushings, Bearing and Thrust Washer Locator
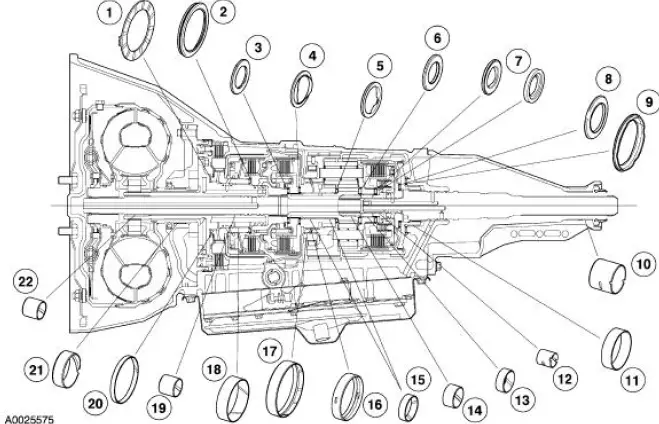
Seals, Rings and Gasket Locator
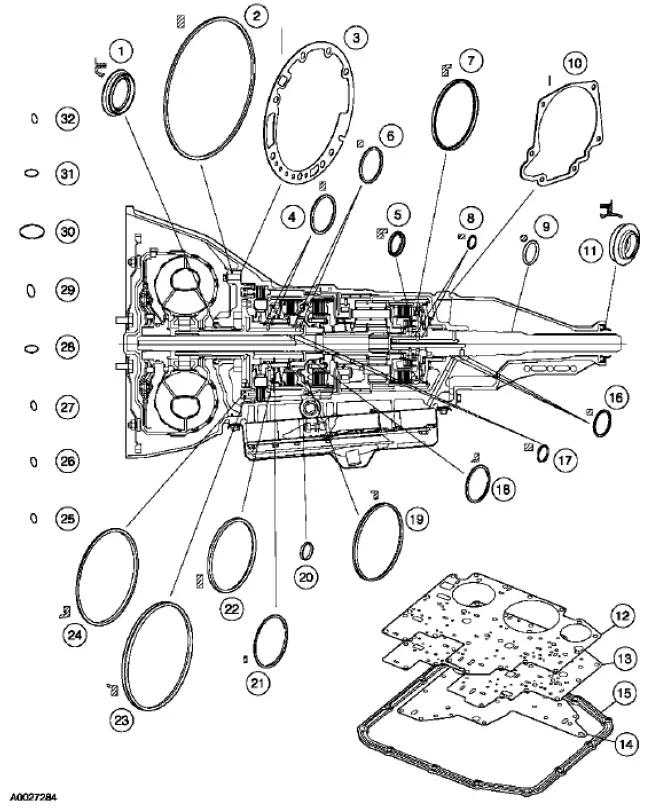
Main Components and Functions
Transmission Main Components - Sectional View
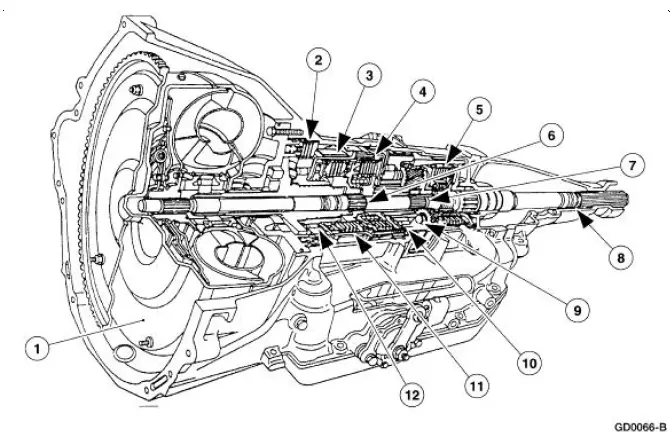
 Range Selection
Range Selection
The transmission has six range positions: P, R, N, (D), 2 and 1.
Park
In the PARK position:
there is no powerflow through the transmission.
the parking pawl locks the output shaft to the ...
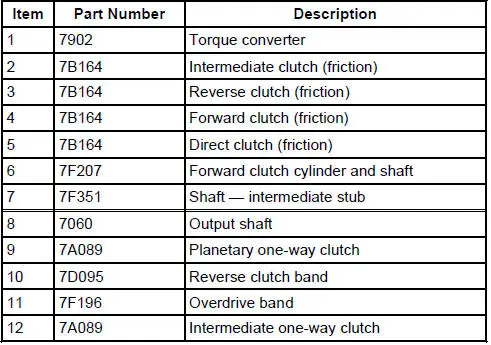
 Torque Converter (Description and Operation)
Torque Converter (Description and Operation)
The torque converter transmits and multiplies torque. The torque
converter is a four-element device:
impeller assembly
turbine assembly
reactor assembly
clutch and damper assembly
...
Other materials:
Valve Tappets
Material
Removal
CAUTION: If removing more than one valve tappet, mark the
components removed for
correct location.
1. Remove the lower intake manifold. For additional information, refer to
Lower Intake Manifold in
this section.
2. Remove the push r ...
Head restraints
WARNING: To minimize the risk of neck injury in the event of a
crash, the driver and passenger occupants should not sit in or
operate the vehicle, until the head restraint is placed in its proper
position. The driver should never adjust the head restraint whil ...
Fuel System (Description and Operation)
Component Location
WARNING: Do not smoke or carry lighted tobacco or open flame of any
type when
working on or near any fuel-related components. Highly flammable mixtures are
always present
and may be ignited, resulting in possible personal injury ...
