Ford Mustang (1999-2004) Service Manual: Electronic Engine Controls (Description and Operation)
The electronic engine controls consist of the following:
- powertrain control module (PCM)
- throttle position (TP) sensor
- idle air control (IAC) valve
- engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor
- cylinder head temperature sensor
- camshaft position (CMP) sensor
- crankshaft position (CKP) sensor
- mass air flow (MAF) sensor
- intake air temperature (IAT) sensor
- heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) - front
- catalyst monitor sensor - rear
- wheel speed sensor
The powertrain control module needs the following inputs to calibrate the engine correctly:
- crankshaft position
- engine rpm
- engine load (manifold pressure)
- atmospheric (barometric) pressure
- engine coolant temperature
The throttle position sensor:
- sends the powertrain control module a signal indicating the throttle plate angle.
- is the main input to the powertrain control module from the driver.
The idle air control valve:
- controls bypass air around the throttle plate at low speeds.
- is controlled by the powertrain control module.
The cylinder head temperature sensor:
- provides a gauge signal for coolant temperature.
- is mounted on rear of LH cylinder head.
- sends the powertrain control module a signal indicating engine temperature.
- resistance decreases as coolant temperature increases.
The camshaft position sensor:
- sends the powertrain control module a signal indicating camshaft position, used for fuel synchronization.
The crankshaft position sensor:
- sends the powertrain control module a signal indicating crankshaft position.
- is essential for calculating spark timing.
The mass air flow sensor:
- sends the powertrain control module a signal indicating mass air flow rate of air entering the engine.
The intake air temperature sensor:
- sends the powertrain control module a signal indicating the temperature of the air entering the engine.
The heated oxygen sensor:
- has the ability to create a voltage signal depending on exhaust oxygen content.
- provides feedback information to the powertrain control module used to calculate fuel delivery.
The rear catalyst monitor sensor:
- monitors oxygen content after the oxygen flows through the catalytic converter.
- provides a voltage to the powertrain control module used to calculate catalytic converter integrity.
The wheel speed sensor:
- sends a signal to the powertrain control module indicating wheel speed.
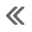 Electronic Engine Controls
Electronic Engine Controls
General Specifications
Torque Specifications
...
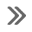 Electronic Engine Controls - Cobra
Electronic Engine Controls - Cobra
Most of the Cobra engine electronic controls are similar to that of
the non-supercharged 4.6L (2V)
engine. These components are as follows:
Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor
Throttle posi ...
Other materials:
Navigation controls
Type 1
WARNING: Driving while distracted can result in loss of vehicle
control, crash and injury. We strongly recommend that you use
extreme caution when using any device that may take your focus off
the road. Your primary responsibility is the safe operation ...
Safety Belt Buckle - Front Seat
Removal
Driver and passenger seat
1. Remove the front seat. For additional information, refer to Section.
2. Remove the nut and the safety belt buckle.
Driver seat only
3. Disconnect the safety belt buckle electrical connector.
Installation
1. To install, ...
Pump - CIII
Special Tool(s)
Teflon Seal Replacer Set
211-D027 (D90P-3517-A) or
equivalent
Removal and Installation
1. Remove the pulley. For additional information, refer to Pulley-CIII Pump
in this section.
2. Remove the bolt and bracket.
3. Disconn ...
