Ford Mustang (1999-2004) Service Manual: Transmission Electronic Control System
The powertrain control module (PCM) and its input/output network control the following transmission operations:
- Shift timing
- Line pressure (shift feel)
- Torque converter clutch
The transmission control is separate from the engine control strategy in the PCM, although some of the input signals are shared. When determining the best operating strategy for transmission operation, the PCM uses input information from certain engine-related and driver-demand related sensors and switches.
In addition, the PCM receives input signals from certain transmission-related sensors and switches.
The PCM also uses these signals when determining transmission operating strategy.
Using all of these input signals, the PCM can determine when the time and conditions are right for a shift, or when to apply or release the torque converter clutch (TCC). It will also determine the best line pressure needed to optimize shift feel. To accomplish this, the PCM uses hydraulic solenoids to control transmission operation.
The following provides a brief description of each of the sensors and actuators used to control transmission operation.
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
The operation of the transmission is controlled by the powertrain control module (PCM). Many input sensors provide information to the PCM. The PCM then controls actuators which determine transmission operation.
Air Conditioning (A/C) Clutch
An electromagnetic clutch is energized when the clutch cycling pressure switch closes. The switch is located on the suction accumulator/drier. The closing of the switch completes the circuit to the clutch and draws it into engagement with the compressor driveshaft. When the A/C clutch is engaged, electronic pressure control (EPC) is adjusted by the PCM to compensate for additional load on the engine.
Brake Pedal Position (BPP) Switch
The brake pedal position (BPP) switch tells the PCM when the brakes are applied. The torque converter clutch disengages when the brakes are applied. The BPP switch closes when the brakes are applied and opens when they are released.
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor detects temperature of engine coolant and supplies the information to the powertrain control module. The ECT sensor is used to control torque converter clutch (TCC) operation. The ECT is installed in the heater outlet fitting or cooling passage on the engine. For engine control applications, the ECT signal is used to modify ignition timing, EGR flow and air-to-fuel ratio as a function of engine coolant temperature.
Ignition Coil - Coil On Plug
The engine uses eight separate coil per plug units. Each coil per plug unit is controlled by the powertrain control module (PCM).
Each coil per plug unit is mounted directly above each spark plug and activates its own spark plug in the correct sequence as controlled by the PCM.
Refer to the Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis (PC/ED) manual for additional information on the ignition system.
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor provides the sequential fuel injection (SFI) system mixture temperature information. The IAT sensor is used both as a density corrector for air flow calculation and to proportion cold enrichment fuel flow. The IAT sensor is installed in the air cleaner inlet tube. The IAT sensor is also used in determining EPC pressures.
Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor
The mass air flow (MAF) sensor measures the mass of air flowing into the engine. The MAF sensor output signal is used by the powertrain control module to calculate injector pulse width. For transmission strategies, the mass air flow sensor is used to regulate EPC, shift and torque converter clutch scheduling.
Transmission Control Switch (TCS) and Transmission Control Indicator Lamp (TCIL)
The transmission control switch (TCS) is a momentary contact switch. When the switch is pressed, a signal is sent to the PCM to allow automatic shifts from first through fourth gears or first through third gears only. The PCM energizes the transmission control indicator lamp (TCIL) when the switch is off.
The TCIL indicates overdrive cancel mode activated (lamp on). When the TCIL is flashing, it indicates electronic pressure control (EPC) circuit shorted or a monitored sensor failure.
Throttle Position (TP) Sensor
The throttle position (TP) sensor is a potentiometer mounted on the throttle body. The TP sensor detects the position of the throttle plate and sends this information to the PCM. The TP sensor is used for shift scheduling, electronic pressure control (EPC) and TCC control.
Digital Transmission Range (TR) Sensor
The digital transmission range (TR) sensor is located on the outside of the transmission at the manual lever. The digital sensor completes the start circuit in PARK and NEUTRAL, and the back-up lamp circuit in REVERSE. The digital sensor also opens/closes a set of four switches that are monitored by the PCM to determine the position of the manual lever (P, R, N, D, 2, 1).
Output Shaft Speed (OSS) Sensor
The output shaft speed (OSS) sensor is a magnetic pickup, located at the output shaft ring gear, that sends a signal to the powertrain control module (PCM) to indicate transmission output shaft speed.
The OSS sensor is used for torque converter clutch (TCC) control, shift scheduling and to determine electronic pressure control (EPC).
Electronic Pressure Control (EPC) Solenoid
The EPC solenoid regulates transmission pressure. EPC valve pressure is used to control line pressure.
Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Solenoid
The TCC solenoid is used to control the apply and release of the TCC.
Shift Solenoid - SSA, SSB
Two on/off shift solenoids provide gear selection of first through fourth gears by controlling the pressure to the three shift valves. One unit containing the two shift solenoids is located in the main control valve body. The shift solenoids are two-way, normally open style.
Solenoid Operation Chart
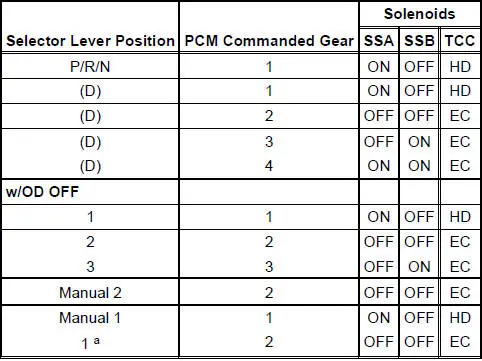
a - When a manual pull-in occurs above a calibrated speed, the transmission will not downshift from the higher gear until the vehicle speed drops below this calibrated speed.
EC = Electronically Controlled
HD = Hydraulically Disabled
Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) Sensor
The transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor is located on the lead frame assembly near the shift solenoids on the main control valve body. It is a temperature-sensitive device called a thermistor. It sends a voltage signal to the PCM. The voltage signal varies with transmission fluid temperature. The PCM uses this signal to determine whether a cold start shift schedule is necessary. The shift schedule is compensated when the transmission fluid temperature is cold. The PCM also inhibits (TCC) operation at low transmission fluid temperatures and corrects electronic pressure control.
Vehicle Speed (VSS) Sensor
The source of vehicle speed (VSS) is model dependent. Possible sources of vehicle speed input are anti-lock brake sensor (ABS), a gear-driven vehicle speed sensor (VSS), or an output shaft speed sensor (OSS). The VSS signal is either an A/C signal whose frequency changes with speed, or an SCP data message depending on the source. Some applications will have both. The vehicle speed signal is an input to various vehicle subsystems such as the powertrain control module (PCM), instrument cluster (speedometer and odometer), speed control system, etc. The vehicle speed source must be operational to enter output state control (OSC) mode for diagnostics.
Regardless of the type of vehicle speed system, the PCM always uses the OSS for transmission and engine control.
 Hydraulic System
Hydraulic System
Fluid Pump
The transmission uses a gerotor-type design front pump support and gear. The
pump provides the
volume of fluid needed to charge the torque converter, main control asse ...
 Diagnostic Strategy
Diagnostic Strategy
Troubleshooting an electronically controlled automatic transmission
is simplified by using the proven
method of diagnosis. One of the most important things to remember is
that there is a defin ...
Other materials:
Spark Plug - Inspection
1. Inspect the spark plug for a bridged gap.
Check for deposit build-up closing the gap between the electrodes.
Deposits are caused
by oil or carbon fouling.
Clean the spark plug.
2. Check for oil fouling.
Check for wet, black deposits on th ...
Degas Bottle
Removal and Installation
1. Drain the coolant. For additional information, refer to Supercharger
Cooling System Draining,
Filling and Bleeding in this section.
2. Disconnect the coolant hoses.
3. Remove the bolts and the degas bottle.
4. To install ...
Cable and Bracket
Removal
1. Raise the vehicle on a hoist. For additional information, refer to
Section.
2. Remove the cable shift from the shifter lever and bracket and discard
the clip.
3. Remove the bolt from the cable.
4. Remove the bolt from the cable.
5. ...
