Ford Mustang (1999-2004) Service Manual: Shift Patterns
Upshifts
Transmission upshifting is controlled by the powertrain control module (PCM). The PCM receives inputs from various engine or vehicle sensors and driver demands to control shift scheduling, shift feel and torque converter clutch (TCC) operation.
Downshifts
Under certain conditions the transmission will downshift automatically to a lower gear range (without moving the gearshift lever). There are three categories of automatic downshifts; Coastdown, Torque Demand and Forced or Kickdown shifts.
Coastdown
The coastdown downshift occurs when the vehicle is coasting down to a stop.
Torque Demand
The torque demand downshift occurs (automatically) during part throttle acceleration when the demand for torque is greater than the engine can provide at that gear ratio. If applied, the transmission will disengage the TCC to provide added acceleration.
Kickdown
For maximum acceleration, the driver can force a downshift by pressing the accelerator pedal to the floor. A forced downshift into a lower gear is possible below calibrated speeds. Specifications for downshift speeds are subject to variations due to tire size, engine and transmission calibration requirements.
Disassembled Views
4R70W Automatic Transmission - Disassembled View
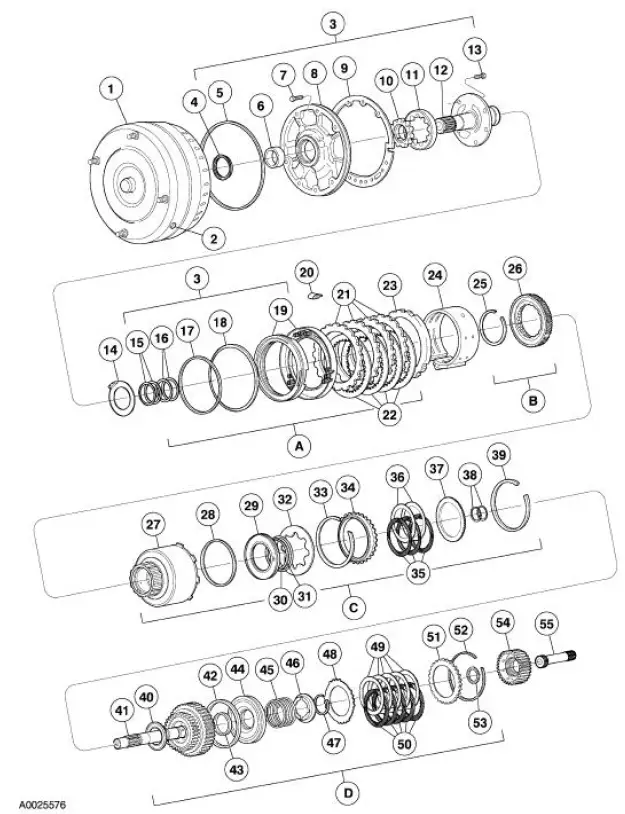
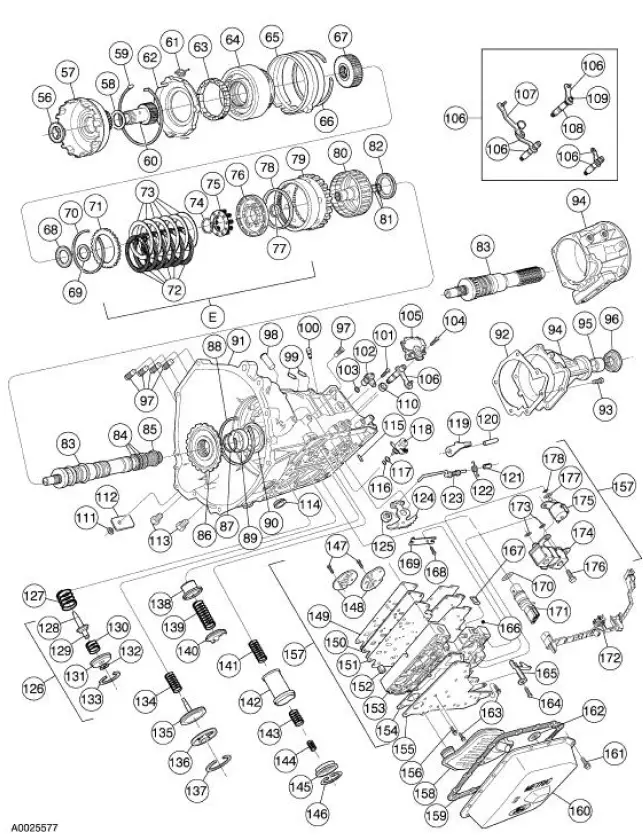
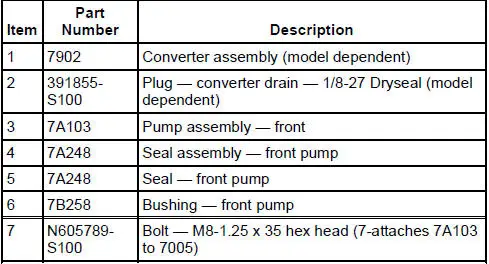
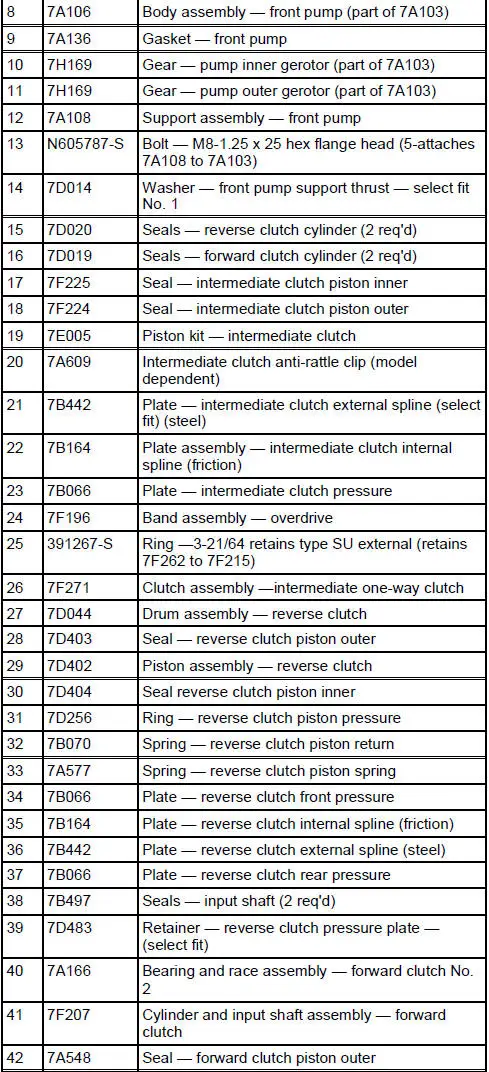
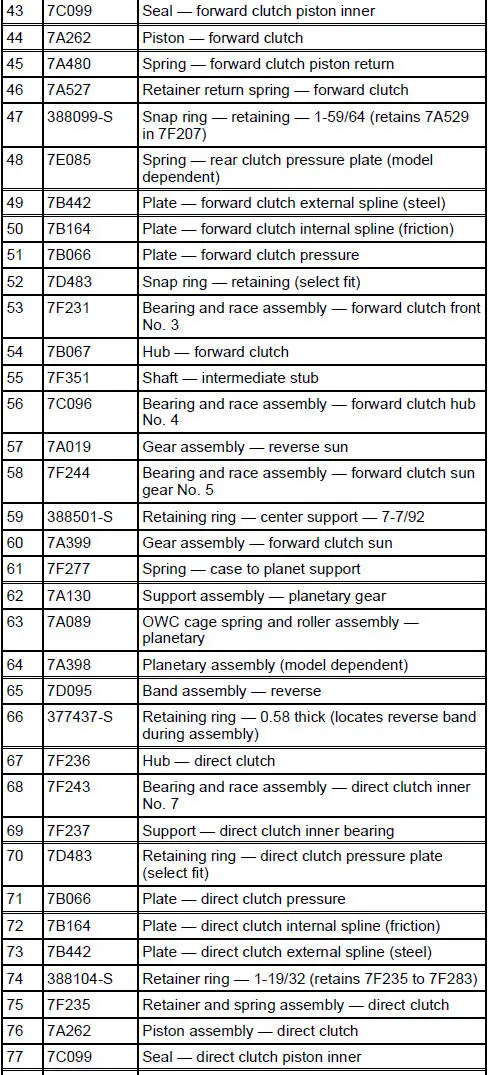
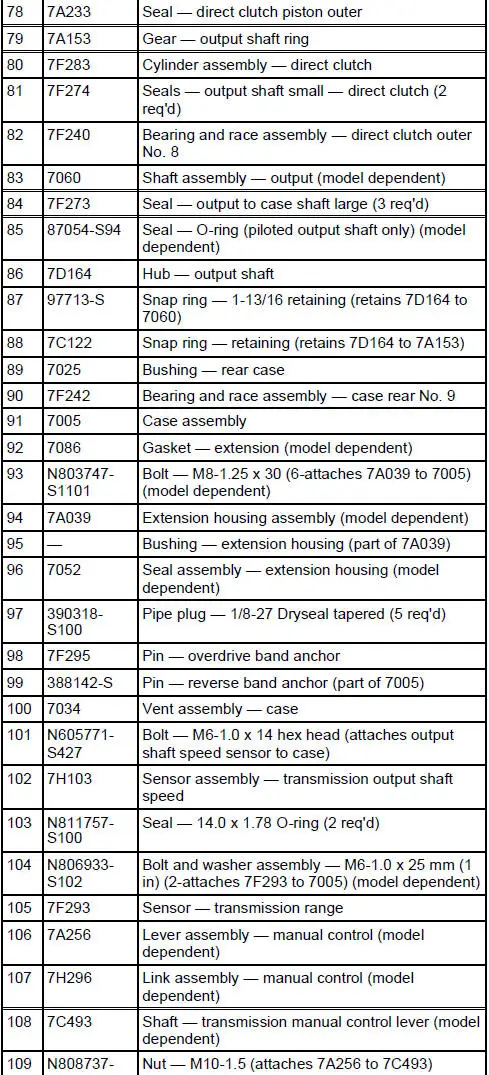
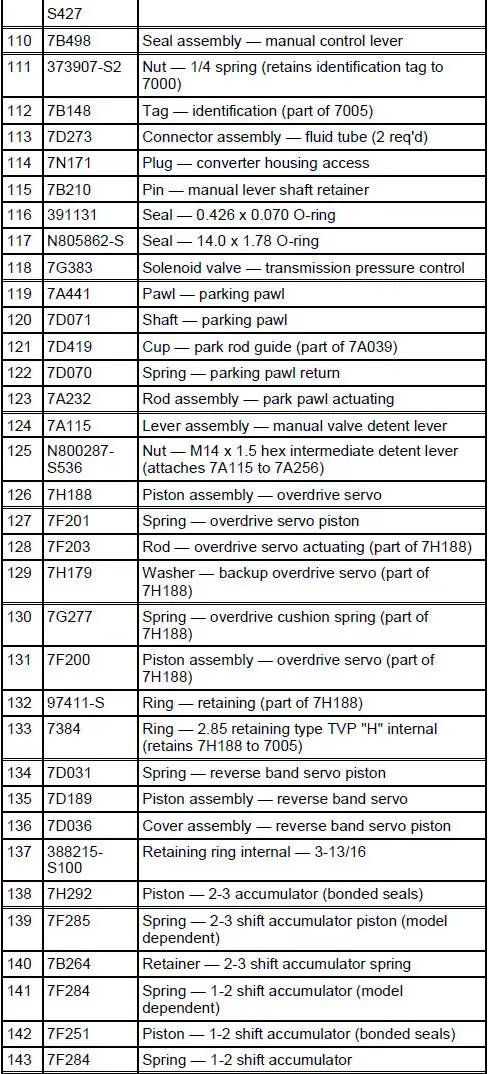
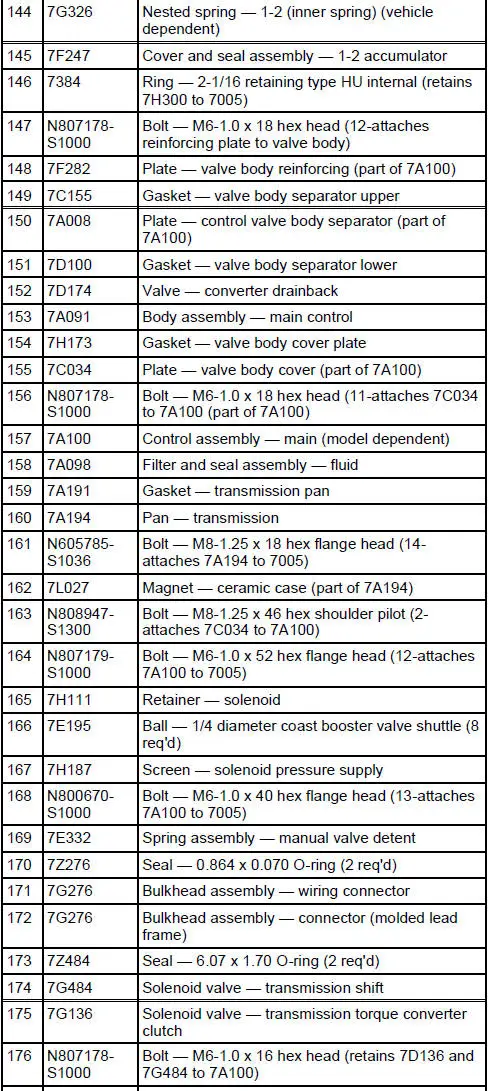
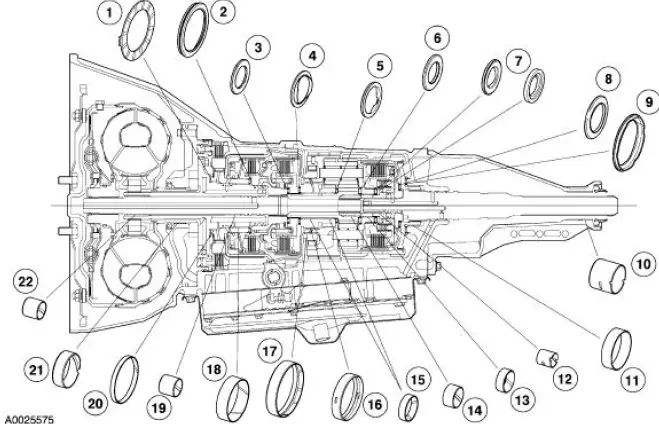
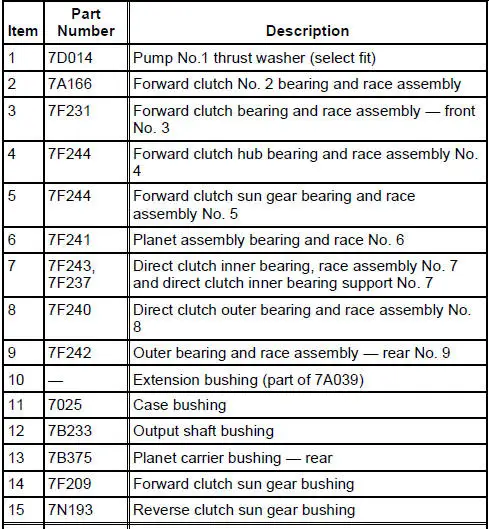
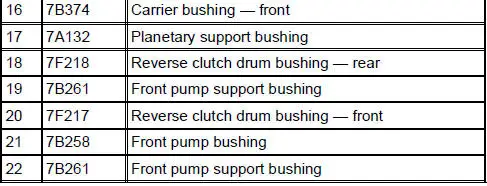
Bushings, Bearing and Thrust Washer Locator
Seals, Rings and Gasket Locator
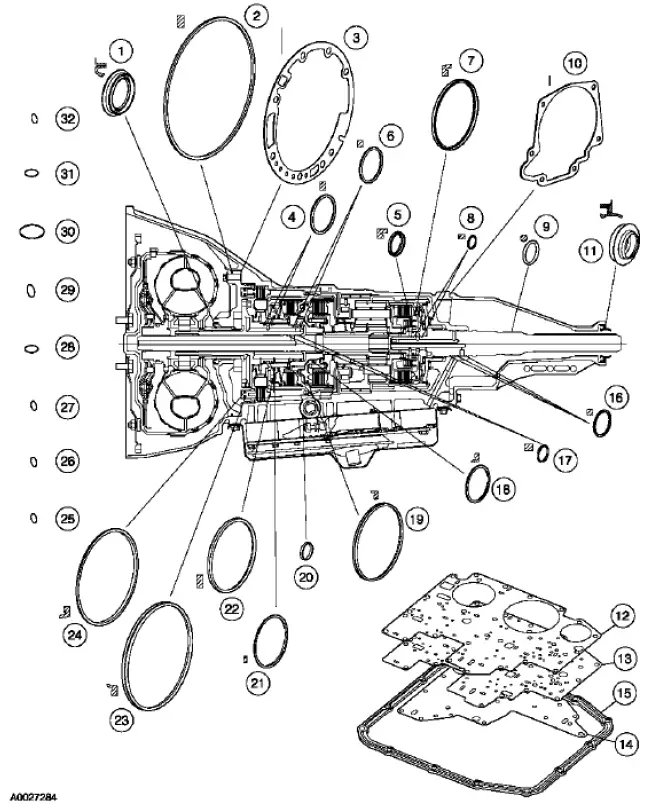
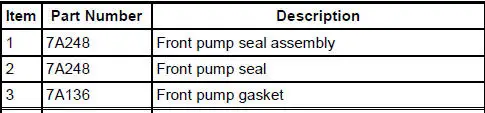
Main Components and Functions
Transmission Main Components - Sectional View
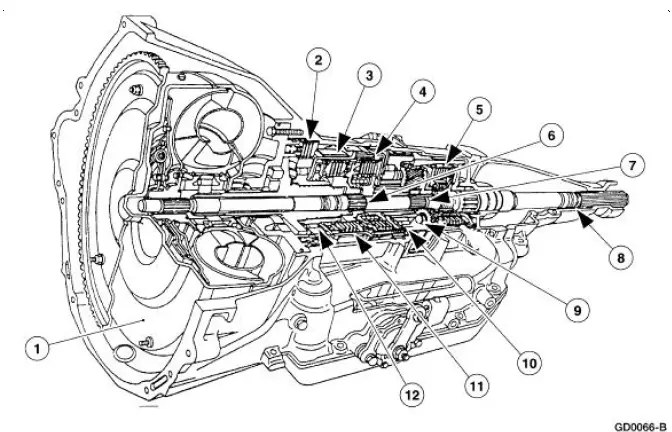
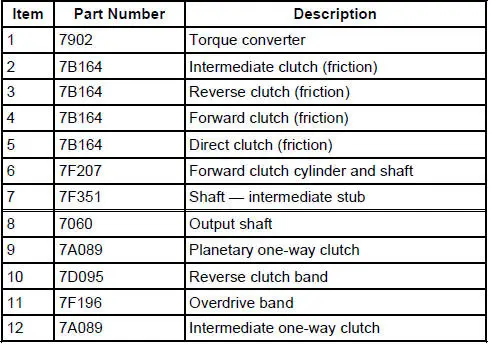
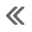 Range Selection
Range Selection
The transmission has six range positions: P, R, N, (D), 2 and 1.
Park
In the PARK position:
there is no powerflow through the transmission.
the parking pawl locks the output shaft to the ...
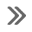 Torque Converter (Description and Operation)
Torque Converter (Description and Operation)
The torque converter transmits and multiplies torque. The torque
converter is a four-element device:
impeller assembly
turbine assembly
reactor assembly
clutch and damper assembly
...
Other materials:
Striker Adjustment
NOTE: After adjusting the door latch striker plate, verify that the
door can be closed easily and fits
tightly.
1. Loosen the door latch striker plate bolts.
2. Reposition the door latch striker plate from side to side or up and down
as necessary.
...
Technical specifications
Wheel Lug Nut Torque Specifications
WARNING: When a wheel is installed, always remove any
corrosion, dirt or foreign materials present on the mounting
surfaces of the wheel or the surface of the wheel hub, brake drum or
brake disc that contacts the wheel. Make ...
Muffler - 4.6L (2V)
Removal and Installation
1. Use a jack to support and lower the rear axle.
2. Remove the upper arm-to-differential bolt.
3. Remove the nut and bolt, and disconnect the rear shock absorbers (18124)
from the axle
housing.
Discard the nut.
4. Lower the r ...
